Same-Day Laser Gingivectomies for Miami Patients
Less bleeding, less pain, and a better smile. Discover the benefits of laser-assisted gingivectomies at CG Smile in Miami.
Excessively "gummy smile" Putting a Damper on Your Smile?
CG Smile performs same-day laser gingivectomies in Miami to help patients uncover a beautiful smile hiding below the surface. With laser-assisted gingivectomies, patients report less pain, faster healing, and practically zero bleeding.
Gingivectomies are part of the CG Smile Makeover, the comprehensive, results-based way patients are achieving the smile they've always wanted. To see how our dentists can completely transform your smile, contact us for a smile consultation today!

What is a Gummy Smile?
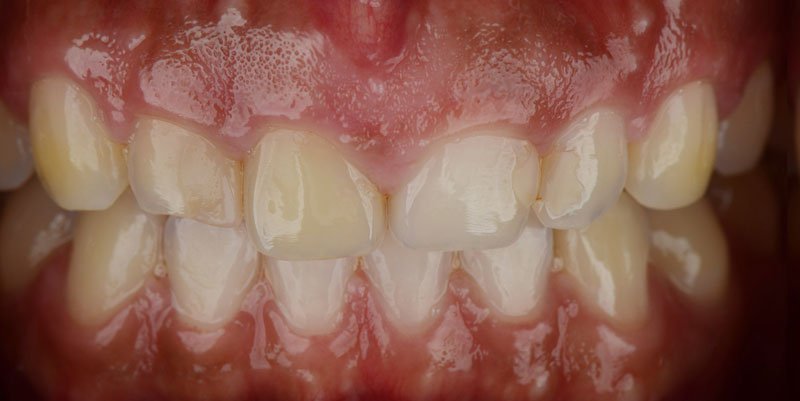
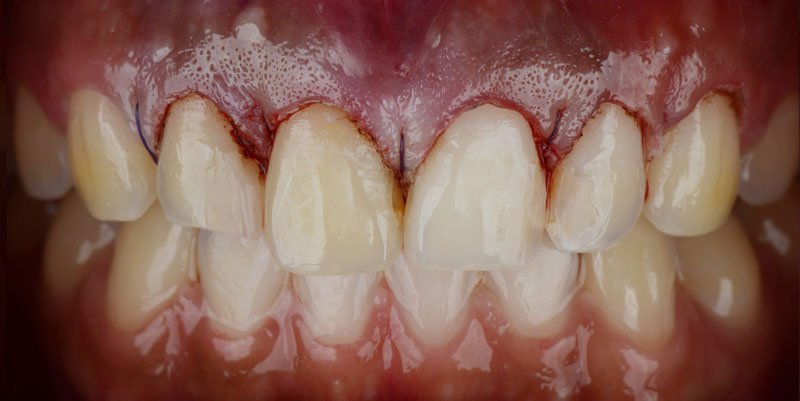
To properly define what a gummy smile is, it might be useful to clarify the basic anatomy of the tooth. The tooth can be broken down into two halves: the crown (the visible portion of the tooth) and the root (the part of the tooth hidden below the gums and jawbone). Typically, the gums will cover the root and a few millimeters of the crown. But, patients with excessive gingival display (gummy smile), the gums (gingiva) may dominate and distract from an otherwise beautiful smile. To correct this, dental practitioners have several treatment options, most notably gingivectomy.Gummy Smile Before & After
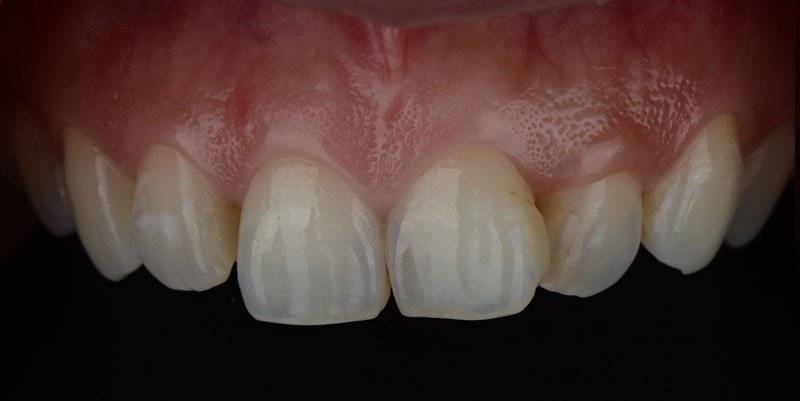
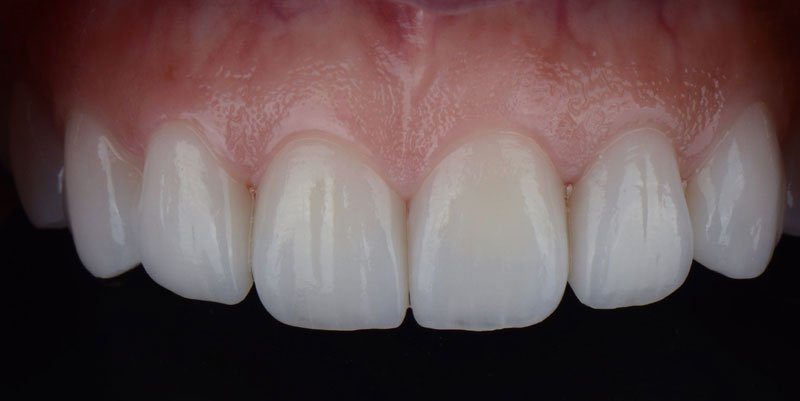
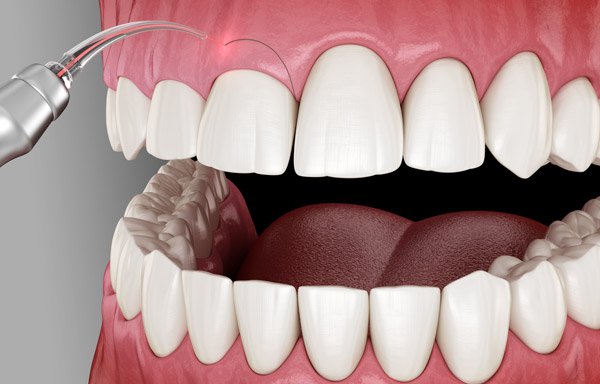
What is a Gingivectomy?
A gingivectomy removes the excess gum tissue and refines the gumline to expose more of the dental crown. Lasers are replacing scalpels in many surgical dental procedures, especially when dentists perform gingivectomies.
Why lasers? The reason lasers are used is that they are able to retain the precision of traditional scalpel techniques while simultaneously cauterizing the area, which in turn promotes more effective healing and better results.
Laser-assisted gingivectomies are used to remove excess gingiva (gum tissue) as well as recontour the gumline for a healthier and/or more attractive smile. Compared to traditional scalpels, with laser-assisted gingivectomies, there is significantly less blood, less pain, and the healing time is often shorter. Plus, by augmenting the wavelength of the diode laser, dentists can vaporize gingival tissue while leaving the enamel of the tooth intact.
What Conditions are Treated with Gingivectomy?
Gingivectomies can be used to correct a number of gum issues and disorders. The most common of these include the following:
Gingivectomy is known by a number of names, such as gum contouring, gum lift, gum reshaping, and gingival sculpting. All of these refer to the same treatment, which involves removing excess gum tissue and transforming the gumline. The ultimate goal of gingivectomy is to alter the appearance and/or the coverage of the gum line, with the end result being a healthier, more attractive smile. Gingivectomies can be performed solely for cosmetic reasons, but a dentist may recommend gingivectomy in cases of advanced gum disease (periodontitis) and other conditions affecting the gums.
What is a Gingivectomy Procedure Like?
Laser-assisted gingivectomies are relatively pain-free and fast-healing compared to the traditional technique of using a surgical scalpel. Here is how a typical gingivectomy procedure takes place: Before an incision is made, the dentist will numb the tissue in the area where the gingivectomy is to be performed. To numb the area, a local anesthetic is injected into the gums. (Local anesthetics are typically not necessary with laser-assisted gingivectomies.)
- The dentist will use either a laser or scalpel to begin incising (cutting) away the excess gum tissue.
- A suction tool is used to remove excess saliva from the mouth (the mouth tends to salivate when foreign objects are present).
- Once the dentist has incised the gum tissue, they will then go back with the laser tool (or scalpel) to further shape, contour, and refine the gumline.
- The dentist may place gauze or a medicated compound on the surface of the gums to encourage healing. There is usually no bleeding with laser-assisted gingivectomies, but blood will likely be present if a surgical scalpel is used.

Scalpel vs. Laser Gingivectomy: a Comparison?
Both metal scalpels and laser-assisted incision tools can be used to perform gingivectomies. These days, scalpel-based gingivectomies are the most common method, but laser-based tools are increasingly finding their place in modern dental offices. To compare these two procedures, we have summarized the findings of the Biomedical and Pharmacology Journal in their research on laser gingivectomies.
- Risk of infection. In clinical studies, it has been shown that patients who receive conventional gingivectomies are more prone to gingival plaque and gingivitis following the gingivectomies when compared to those who received laser-assisted gingivectomies.
- Pain and discomfort. Patients report that laser-assisted gingivectomies are associated with less pain and discomfort than with scalpel-based gingivectomies.
- Post-surgical bleeding. With scalpel-based procedures, there is always some level of bleeding. Since laser-assisted gingivectomies actually cauterize the wound, bleeding is kept to an absolute minimum.
- Cost. As a newer technology, laser-assisted gingivectomies tend to be more expensive than conventional gingivectomies. Also, insurance coverage may vary from one procedure to the next. Therefore, it’s important to check your coverage when evaluating the different procedures available.
There are many factors that come into play when deciding on a type of gingivectomy. Consult with your dentist to determine which form is most appropriate for your dental condition.
Recovering from Gingivectomy
Gingivectomies are outpatient procedures. Since only a local anesthetic is used, you do not need a designated driver. You may return to work or home directly after the appointment. Some pain and discomfort can be expected in the hours following the procedure. Analgesics such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen can be used to alleviate the discomfort.
Your dentist may caution against eating hard foods that might disrupt the healing process.
- Physical activity. Once your gingivectomy is complete, you may resume normal activities. For the next 72 hours, you should avoid any type of sport or aerobic activity.
- What to eat and drink. You should wait to eat until the local anesthetic wears off (your tongue may still be numb). Try sticking to high-protein soft foods such as eggs and yogurt. Avoid using straws until the wounds have completely healed.
- Managing pain and discomfort. You may notice some pain and/or discomfort in the gums and jaw over the next several days. It might not be apparent when you first leave the office, but will likely become apparent when the local anesthetic wears off. In some cases, the dentist will prescribe a prescription-strength non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medication (NSAID). Be sure to take this as prescribed. Anti-inflammatories are useful in keeping down the swelling, as well as reducing the sensitivity of the surgical wound. Applying cold packs and taking pain relievers should be useful in reducing the swelling and alleviating any discomfort you may have.
- Bleeding. Post-surgical bleeding is more common following conventional gingivectomies than laser-assisted gingivectomies. If a scalpel was used to perform your gingivectomy, some bleeding can be expected for the next several of days. If bleeding persists or is overly excessive, contact your dentist for a follow-up.
- Avoid excessive pressure on the surgical site. If you typically wear a nightguard, clear aligner, or CPAP mask at night, mention this to your dentist. Keeping pressure off the surgical site is important to the healing process.
- Brushing and flossing. You can continue to brush and floss all areas unaffected by the gingivectomy. Do not attempt to brush the areas of the gums that received the gingivectomy as this can dislodge the blood clots and may pose an infection risk. You may dab the healing gums with a specialized gum care product containing chlorhexidine, such as Peridex®.
- Rinses. Saltwater rinses are beneficial in helping eliminate bacteria from the mouth. Most dentists recommend dissolving a half-teaspoon of salt in eight ounces of warm water. Antiseptic alcohol and peroxide-based mouthwashes should be avoided as these can disrupt the healing process.
- Conventional gingivectomies. If a conventional (scalpel-based) gingivectomy is performed, then some blood spotting can be expected for the next 48 hours. Follow the dentist’s advice on caring for the wound, especially in terms of changing the dressings. Most pain and discomfort should subside in about a week.
- Take medication as prescribed. If antibiotics or other medications are prescribed, be sure to take these as directed by your dentist.
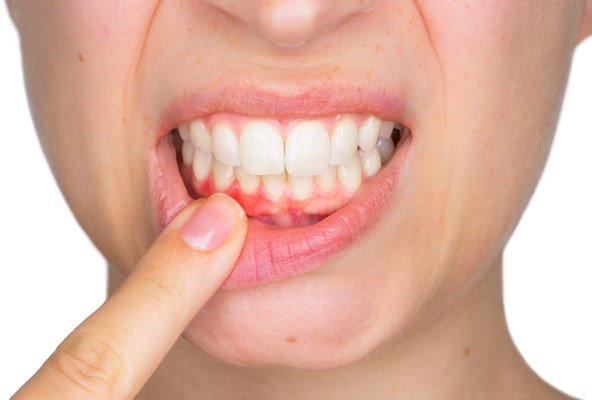
Know the Signs of Gingivitis
Gingivectomy is a treatment option for those with gingivitis. Knowing the signs of this disease can help you take remedial action and avoid surgery. Gingivitis is the inflammation of the gums. When the gums become inflamed, the connections between the gums, crown, and root become loose. This can lead to tooth loss and additional periodontal issues. It’s important to note that those with gingivitis may not notice any pain or discomfort. If you notice any of the following symptoms, schedule an appointment with your dentist:
- Gum tenderness
- Swelling of the gums
- Pus along gumline
- Tender gums
- Tooth looseness (wiggling)
- Blood spots after brush or flossing
- Receding gumline
- Bad breath (halitosis) or foul taste
Have you experienced any of these symptoms?
Gingivitis is the first stage of advanced periodontal disease and should be taken seriously. Schedule an appointment with your dentist today.